
When building a server, one of the most important questions you will face is choosing the right storage solution. The storage you choose can have a significant ...
3v-Hosting Blog
7 min read
The “404 Not Found” error is one of the most recognizable and frequently encountered HTTP status codes on the Internet. Whether you are a website owner, developer, or regular user, you have probably encountered this error more than once while browsing web pages. Despite its prevalence, many people do not fully understand what a 404 error is, why it occurs, and how to fix it. In this article, we will take a detailed look at this topic, what a 404 error is, the reasons for its occurrence, and the consequences of this error for website administration. And, of course, we will describe several methods for fixing it.
Before we look at the specifics of the 404 error code, it is important to understand the context in which it operates, namely HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) status codes. These codes are standardized responses sent by servers to indicate the result of a client request. They are divided into five categories, which start with numbers from one to five:
A 404 error belongs to the 4xx category and means that the client made a valid request, but the server cannot find the requested resource.
Now let's take a closer look at the 404 response code.
A 404 error occurs when a client (e.g., a web browser) requests a resource (e.g., a web page) that the server cannot find. This error does not mean that the server is down or malfunctioning; rather, it indicates that the URL entered does not correspond to any resource currently available on the server.
The full error message usually looks like this: “404 Not Found” or “Error 404 Not Found.” This response is sent by the server when it cannot find the requested content. The server has successfully processed the request, but the requested resource (e.g., a specific web page, image, or file) is not available, usually because it has been moved, deleted, or the URL has been entered incorrectly.
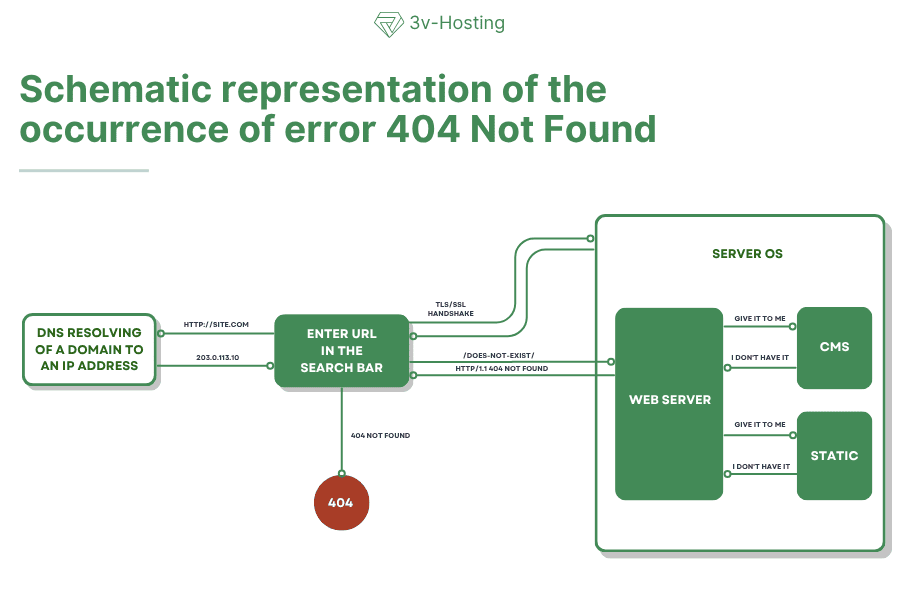
To better understand the nature of a 404 error, it is helpful to break down what happens between the moment a user enters a website address in the browser bar and the appearance of the “404 Not Found” page.
The user enters the URL
The browser breaks down the entered address into parts: the protocol (http or https), the domain name (site.com), the port (default 80 or 443), and the path to the resource (/page.html or /blog/article-1/).
DNS resolution of the domain to an IP address
The browser queries the domain name system (DNS) to obtain the IP address of the server hosting the website.If the domain is found, the DNS server returns the IP (for example, 203.0.113.10). If the DNS is configured incorrectly, an error may occur even before step 404, but in a normal situation, the resolution is successful.
Establishing a network connection with the server
Next, the browser establishes a connection with the server using the TCP protocol. With https, an encrypted channel (TLS/SSL handshake) is set up on top of TCP. After successfully establishing a connection, the browser can send HTTP requests.
Sending an HTTP request to a specific resource
The browser forms and sends a request in approximately the following form:
GET /does-not-exist/ HTTP/1.1 Host: site.com User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 ... Accept: text/html,application/xhtml+xml
Key elements of the request: method (GET), path (/does-not-exist/), and Hostheader, which tells the web server which site the request belongs to (especially important for virtual hosting).
Request processing by the web server and/or application
The request goes to the web server (Nginx, Apache, LiteSpeed, etc.). There are two possible scenarios: If the requested file is not found and the CMS reports that such a route (URL) does not exist, the server comes to the only possible conclusion - the requested resource does not exist.
The server searches for a static file along the specified path (for example, root /var/www/html; and the file /var/www/html/does-not-exist/index.html),
The server forwards the request to the application or CMS (PHP script, framework, WordPress, Django, etc.), which decides for itself whether the requested page exists.
Forming a response with code 404
As a result, the server generates a response:
HTTP/1.1 404 Not Found Content-Type: text/html; charset=utf-8 Content-Length: ... ...
After the headers, the server sends the HTML code of the error page. This can be a standard minimalist web server page or a custom 404 page for the site.
Displaying the error page in the browserThe browser receives the response, sees the status code 404 in the status bar, and displays the received HTML as a “Not Found” page. To the user, it looks like a familiar 404 page with text stating that the resource is missing.
Essentially, a 404 error can occur in two places:
location/rewritedid not match),Therefore, if you carefully analyze this chain, it becomes quite easy to find the cause and correctly configure the server, redirects, or CMS. To make it even easier, we have provided a simplified diagram of how a 404 error occurs.
Several main factors can lead to the “404 Not Found” error, including:
When a 404 error has already occurred, it is important not to limit yourself to your guesses and a simple visual inspection of the site. It is much more productive to go through a simple checklist and perform diagnostics, from the request to the server to the CMS and file permissions. Below is a sequence of steps that will help you quickly locate the problem and ultimately fix it.
First, make sure that the resource really returns a 404 and not some other error or redirect.
curl -I https://site.com/does-not-exist/
Pay attention to the line HTTP/1.1 in the response:
HTTP/1.1 404 Not Found - a real 404 error;HTTP/1.1 301 Moved Permanently or 302 Found - a redirect is in progress, check the final URL;HTTP/1.1 200 OK for a clearly non-existent page - a potential soft 404, which can negatively affect SEO.
To view the full response, you can use the command for a more detailed response:
curl -v https://site.com/does-not-exist/
This will help you see the redirect chain and server headers.
The next step is to see what the server sees when processing a request. Nginx and Apache logs usually clearly show which URL was requested and with which code it was returned.
Example of a line in the Nginx access log:
203.0.113.5 - - [12/Nov/2025:10:15:23 +0000] “GET /does-not-exist/ HTTP/1.1” 404 612 “-” “Mozilla/5.0 ...”
Example for Apache:
203.0.113.5 - - [12/Nov/2025:10:15:23 +0000] “GET /does-not-exist/ HTTP/1.1” 404 612 “-” “Mozilla/5.0 ...”
There are a couple of commands that will help you work with logs. For example, to display the last hundred lines of the Nginx access log, use the tailcommand:
tail -n 100 /var/log/nginx/access.log
To find only those requests in the log that contain the text “404”, run:
grep “ 404 ” /var/log/nginx/access.log | tail -n 50
The logs can help you understand:
If the logs show that the request does not reach the correct application or folder at all, it is worth checking the virtual host configuration.
Basic example of a serverblock:
server {
server_name site.com;
root /var/www/site.com;
location / {
try_files $uri $uri/ /index.php?$args;
}
location ~ \.php$ {
include fastcgi_params;
fastcgi_pass unix:/run/php/php8.2-fpm.sock;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
}
}
What to pay attention to first:
root specified correctly?location intercepting the desired path and returning a 404?try_files for the CMS/framework that should handle “pretty” URLs?
After any changes, be sure to check the configuration and restart the service:
sudo nginx -t sudo systemctl reload nginx
The same logic applies to Apache (directives DocumentRoot, RewriteRule, ErrorDocument).
Sometimes a resource physically exists, but the server cannot read the file due to incorrect permissions for that resource, which ultimately also leads to a 404 or even 403 error.
The quick permission check command looks like this:
ls -l /var/www/site.com
There are several general recommendations that, if followed, will help you avoid most problems:
755 permissions;644 permissionswww-data).If the application or CMS generates files dynamically (e.g., images, cache), make sure that the server has write permissions to the relevant directories.
If the site runs on a CMS (WordPress, Joomla, Drupal) or framework (Laravel, Symfony, Django), the 404 error may occur not at the web server level, but within the application itself.
What to check:
.htaccess and restore routing.Finally, it is important to make sure that the error is not only reproducible locally:
If the resource opens correctly from external services but not for some users, the problem may be with local DNS settings, provider caching, or geographic routing. In this case, you can try clearing your browser cache and using a VPN to check.
At first glance, a 404 error seems quite simple and straightforward: the page cannot be found. However, search engines distinguish between two fundamentally different scenarios - Hard 404 and Soft 404 - and their impact on SEO varies significantly.
Hard 404 is a classic situation where the web server honestly reports that the resource at the specified address does not exist. The response contains the correct status 404 Not Found, and the search robot receives a clear technical signal that there is nothing to index. Such errors are normal for any site - after all, pages are deleted, materials become outdated, and links may lead to content that no longer exists.
Soft 404 works completely differently. Here, the server returns a “successful” code - for example, 200 OK or redirects the user via a 301/302 chain - but Google still classifies the page as missing. Essentially, this is a situation where the page technically exists but is actually useless, for example, it has too little content, only displays a template with the message “nothing found,” the CMS category is empty, or a non-existent URL leads to the home page instead of the correct error. In such cases, the search engine considers that the site is misleading it.
To make the difference clear, here is a brief comparison:
| Criterion | Hard 404 | Soft 404 |
|---|---|---|
| Response code | 404 Not Found | 200, 301 or 302 |
| Who determines the status | Server | |
| Does the page exist | No | May exist physically |
| SEO impact | Moderate | Strongly negative |
| Needs fixing | Not always | Almost always |
| Indexing behavior | Not indexed | May be misindexed or excluded |
Soft 404s most often appear in Google Search Console in the indexing section. Search Console usually marks them as “Page has a soft 404” or “Page does not contain useful content.” In practice, such errors occur on empty sections, filters, internal search results, thin or automatically generated pages, as well as where the CMS or server returns incorrect HTTP codes.
Soft 404s most often affect a site's ranking. While a hard 404 is a normal signal that a page does not exist, Google perceives a soft 404 as a quality issue. They waste crawl budget, make it difficult for search engines to determine the structure of the site, and can eventually reduce trust in the domain. In extreme cases, this leads to a drop in visibility even for pages that are not directly related to the error.
Soft 404s can be identified fairly quickly. If you run a simple query curl -I https://example.com/страница/ and see a 200 code when the page is actually empty or looks like an error, this is a clear sign of a soft 404. Similarly, it is worth paying attention to cases where a non-existent URL suddenly takes the user to the home page or another irrelevant section, as Google considers such redirects to be an attempt to hide the absence of a page.
Although a single 404 error on a website may seem insignificant, frequent occurrences of such errors can have significant negative consequences for the website, especially in terms of user experience and SEO (search engine optimization).
From a user's perspective, a 404 error can be unpleasant. It interrupts the browsing flow and can create the impression that the website is poorly maintained or unreliable. This can lead to an increase in bounce rates, where users leave the site after viewing only one page, potentially reducing overall user engagement and significantly impacting the behavioral factors that Google considers when ranking a site in future search results.
404 errors can also negatively impact a website's SEO performance, as we briefly mentioned above. Search engines such as Google interpret frequent 404 errors as indicators of poor website service. This can lead to a lower ranking on search engine results pages (SERPs). In addition, search engines may de-index pages that frequently return 404 errors, resulting in a loss of traffic.
However, it is important to note that not all 404 errors are harmful to SEO. With proper handling using appropriate error pages and redirects, their impact can be minimized. Nevertheless, allowing too many unresolved 404 errors can damage the overall visibility and authority of a website.
Effectively fixing all 404 errors on a website requires a comprehensive approach. Below are some strategies that can be used to do this:
Sometimes, fixing a 404 error is as simple as correcting a typo in the URL. Website administrators should regularly check the accuracy of their URLs and ensure that all internal and external links point to the correct resources.
When a web page is moved or deleted, it is important to set up a redirect (301 redirect) from the old URL to the new one. A 301 redirect is a permanent redirect that transfers the SEO value of the original URL to the new URL, helping to maintain the site's ranking in search engines.
Setting up a 301 redirect depends on the server environment: In Apache, this can be done by adding a redirect rule to the .htaccess file, and in Nginx, you need to add a rewrite rule to the “server” block configuration.
A customized 404 error page can improve the user experience by providing useful information when a 404 error occurs. Instead of displaying a generic error message, a custom 404 page can include links to other parts of the site, a search bar, or a message encouraging users to check the URL or contact support.
Creating a custom 404 page typically involves changing the server configuration to point to a specific HTML file that serves as the error page. For example, on an Apache server, you would add the following line to the .htaccess file:4. Monitor 404 errors
Regularly monitoring your site for 404 errors allows you to quickly identify and fix them. Tools such as Google Search Console, Screaming Frog, or server logs can help you track 404 errors on your site. Once you find them, you can take steps to fix the errors, such as setting up redirects or fixing broken links.
Broken links are a common cause of 404 errors. Regularly auditing your site for broken internal and external links ensures that users can always access the content they are looking for. Tools such as Broken Link Checker can automate this process by scanning your site for broken links.
Incorrect server configuration can lead to 404 errors. It is essential to ensure that your server is configured correctly and that all necessary files (e.g., .htaccess) are in place. This step is especially important for websites that are frequently updated or migrated.
Preventing 404 errors requires constant vigilance and best practices in website management. Here are some tips to reduce the likelihood of 404 errors on your website:
Choosing a reliable content management system (CMS) and updating it regularly can reduce the risk of 404 errors. A well-maintained CMS ensures that URL structures are preserved and that updates do not inadvertently create broken links.
Conducting regular website audits can help identify and fix potential issues before they lead to 404 errors. This includes checking for broken links, verifying that redirects are working correctly, and ensuring that your content is organized properly.
Maintaining a consistent URL structure helps prevent 404 errors. Avoid renaming or moving files and pages unnecessarily. If changes are necessary, ensure that the correct redirects are in place.
If your site has multiple administrators or content managers, it is important to train them on best practices for linking to content. This includes checking URLs before publication and understanding the consequences of moving or deleting content.
Understanding the causes of 404 errors is important for anyone involved in web development, administration, or content management. Although often perceived as a minor inconvenience, frequent 404 errors can have serious consequences for both user experience and SEO. By understanding the main causes of these errors and implementing strategies to prevent or fix them when they occur, you can ensure high reliability and user-friendliness for your website.
Effective management of 404 errors includes regular monitoring, proper server configuration, consistent URL structure, and the use of custom error pages. In addition, setting up 301 redirects for moved or deleted content ensures that users and search engines are directed to the correct pages, preserving the value of your site for SEO.
Favicon - what it is, why you need it, and how to set it up correctly for all browsers and devices. Sizes, formats, SEO impact, and common mistakes in one guide...

Switching users in Ubuntu: su, sudo, sudo -i, sudo -u, and SSH. A practical guide to working securely with permissions, environments, and sessions on servers an...

Managing ports on VPS and dedicated servers: how to check open ports, configure your firewall correctly, avoid common mistakes, and improve infrastructure secur...